Medical imaging is most frequently associated with radiography. With X-rays being the oldest medical imaging technology, it’s totally understandable they are still a trusted and well-explored way to get complete and reliable information about patients’ health.
The advent of digital imaging softwares contributed to more technology advancements appearing in this field. Among them is a three-dimensional imaging and printing, picture archiving and communication system (PACS). Artificial intelligence and augmented reality boost radiology to help clinicians achieve diagnosis precision and automate routine operations with images. In this article, we’ll explore some of the advanced medical imaging technologies to prove that the future of medical imaging has already come.
The evolution of medical imaging technologies in radiology
The 20th century can be rightly seen as the period of radiology’s dynamic development. After Wilhelm Roentgen made the first X-ray in 1885, things went quite dynamically. It won’t compete with the current pace of development thanks to digital technologies. However, the most important technologies that we use nowadays were invented during the 20th century: radiographs, MRI, CT, ultrasound, mammography, and others.
Thanks to modern healthcare IT solutions all of these technologies are getting enhancements on a constant basis. Radiologists are able to conduct an in-depth analysis of medical images received from medical modalities.
Another good point here is that healthcare software development services develop solutions that facilitate the work with medical images and their examination. An example of such a solution is a picture archiving and communication system (PACS).
What is PACS and why does your clinic need it?
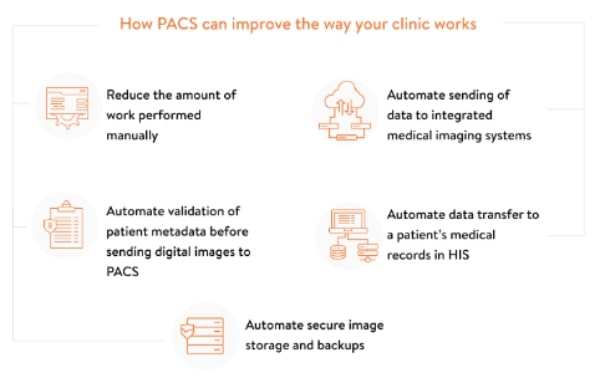
Hospitals implement PACS to ease the work with ready-made medical images. Instead of using local storage in the radiology departments, by introducing PACS, clinics opened a new way of retrieving and storing medical images. A PACS radiology system minimizes people’s intervention in the process of initiating an examination session, getting results, and storing them.
The PACS architecture predefines the way in which healthcare providers work with the system. Hospitals use the PACS server with all the images stored, PACS Client is a radiologist tool that helps them access images, and DICOM workstations are for analyzing images and making reports.
Besides helping radiologists with analyzing medical images, PACS also works as a mediator. The system helps to:
- upload a Worklist to the medical modality
- initiate an examination session
- receive and store medical images in its archive automatically
- analyze medical images
It’s a common practice to use DICOM viewers that help radiologists examine pictures and manipulate them. For instance, they can zoom them in and out, apply advanced filters, make notes, measurements, and so on.
Advanced visualization solutions
If earlier radiologists could carry out pretty basic research, such as viewing images, measuring problematic areas, zooming in and out, now advanced medical digital imaging systems are capable of providing conditions for 3D imaging, image fusion, real-time imaging, intensity projecting, and the list goes on.
Let’s consider them in detail on real-life examples:
#1: syngo.via from Siemens is an enterprise imaging and reporting solution. It provides extensive capabilities for image interpretation, reporting, and data management. Thanks to using artificial intelligence, Sygno guarantees improved image precision in diagnostics and image processing.
#2: IntelliSpace Portal from Philips is an advanced medical visualization platform that supports the analysis, interpretation, and presentation of patient data. It’s a single solution for image post-processing that greatly improves diagnosis precision and simplifies radiologists’ work.
#3: Vitrea Vision from Canon is one of the advanced enterprise solutions that provides access, accuracy, and collaboration for hospitals and healthcare professionals. Vitrea Vision offers solutions for standardization and consolidation of radiology data, provides real-time access to consolidated imaging information, and improves diagnostics quality.
Each of the solutions mentioned above regularly receives updates aimed at improving diagnosis precision and patient care.
The future of medical imaging technologies
The digital world is dynamically changing. We have new technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and others implemented into various spheres and domains. Radiology and, specifically, medical imaging technologies aren’t an exception. In the future implementation of such technologies will be more widespread and help to work with data in various ways. For instance, they will assist in analyzing huge data sets faster than a human does, automatically compare a patient’s medical images of different dates as soon as new data is received. AI can potentially help identify neoplasms better than people do.
- Cloud PACS solutions. Another tendency we can experience even now. Many PACS software solutions are installed locally throughout the clinic. However, there are vendors who offer cloud PACS solutions. They help step outside of the locality factor and make functionality and data be available from any location and device. Another value of cloud-based PACS solutions is storage. With cloud storage providers involved, hospitals can increase the amount of free space on cloud disks as the circumstances require. Cloud space is also significantly cheaper than local storage. Besides, you can choose a suitable, HIPAA-compliant provider to make sure that all of the patients’ personal information is strictly protected.
- 3D and virtual reality. Empowering medical scans like MRIs and CT with 3D and virtual reality technologies is also considered a trend that is becoming reality right now. Cinematic rendering allows the augmented reality software to create a realistic picture of human organs. With medical images having texture, radiologists can, for example, examine tumors.
- Mobile imaging. The technologies of mobile or intraoperative imaging help surgeons analyze tissues and allow them to make cuts and dissections precise. Making use of the imaging intraoperative techniques helps doctors do biopsies or control catheters insertion.
This should be enough to understand that medical imaging solutions are gaining momentum. Each year there appear more techniques to help clinicians and radiologists improve patient care and perform critical medical operations.